OFDM
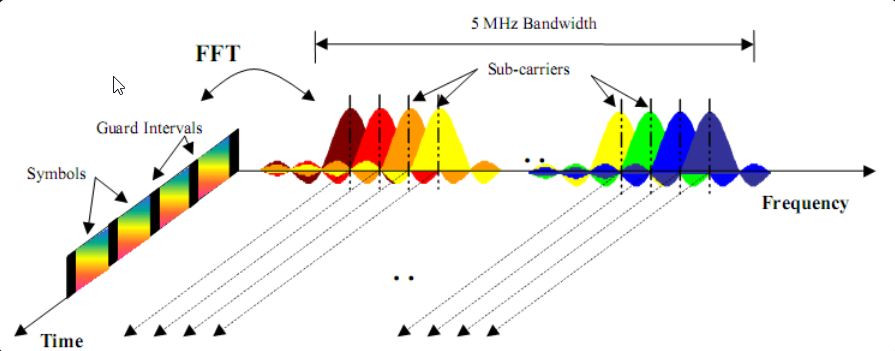
IQSTAR custom OFDM modulation is a flexible signal-creation tool that can quickly and easily generate OFDM waveform for component, transmitter, and receiver test. This tool allows to set parameters such as OFDM FFT length, guard interval, guard sub-carriers, preamble, pilot, and data resource modulation type (Arbitrary binary sequence, QPSK, 8PSK 16/32/64/128/256/512/1024/2048/4096 QAM). Set flexible resource mapping with preamble, pilot, and data resource block types–Easily add variable Cyclic Prefix (CP) length or Windowing and generate Zadoff-Chu sequence.
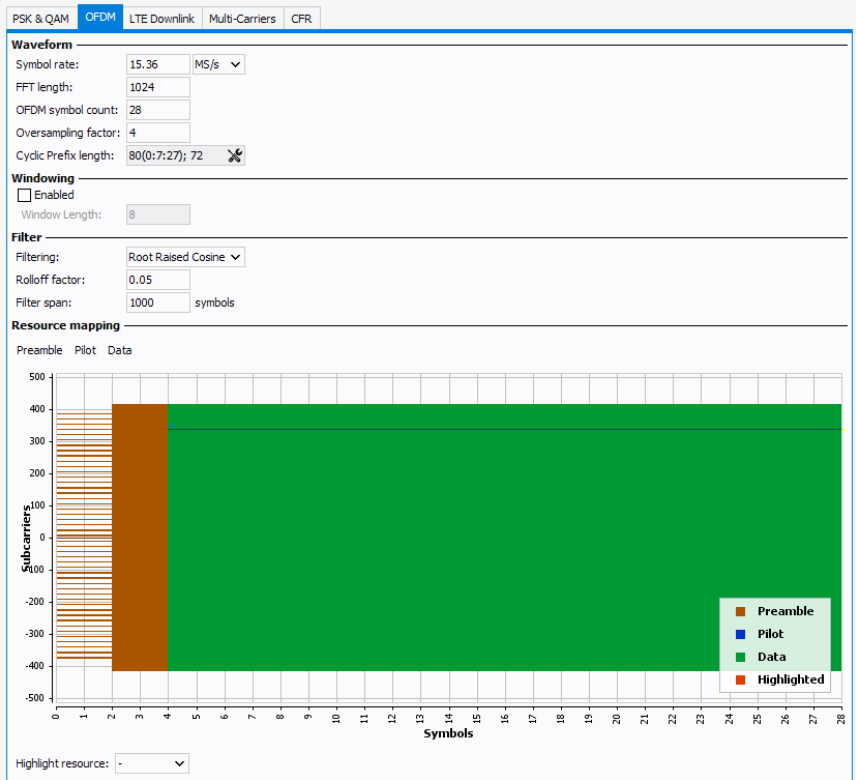
Waveform settings
- Symbol rate : determines the rate (frequency) at which symbols occur in samples per second. Minimum value >0.
- FFT Length: Set the FFT length of the OFDM signal. This value will be clipped to the nearest power of 2.
- OFDM symbol count: Set the number of OFDM symbols in a frame, which usually includes preamble symbols and data symbols (Minimum value >0).
- Oversampling: Defines the oversampling factor. The final waveform sampling rate will be equal to Symbol rate x Oversampling (Minimum value >0).
- Cyclic Prefix Length: Opens the Cyclic Prefix Length editor
(
 ) for configuring the length of the OFDM symbols
within a frame. You can set each symbol individually or use a preset configuration.
) for configuring the length of the OFDM symbols
within a frame. You can set each symbol individually or use a preset configuration.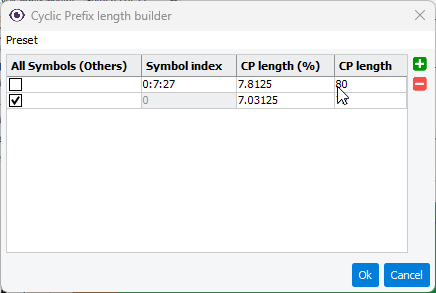
- To configure by individual symbol, use a comma (,) as the delimiter. For example, 0,1,2,3.
- To configure by a range of symbols, use a colon (:) to indicate the start symbol index and the end symbol index. For example, 3:10 means symbols 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
- To configure by a certain step, use two colons (:) to indicate the start symbol index, the step, and the end symbol index. For example, 0:5:20 means symbols 0,5,10,15,20.
-
Note: OFDM symbol count x FFT Length define the matrix size of the resources map grid.
Windowing
The use of the IFFT within the OFDM modulation constitutes the use of a rectangular pulse shape. This use of the IFFT means that discontinuities occur from one OFDM symbol to the next, resulting in out of band emissions. The discontinuities between OFDM symbols can be reduced by using windowing, which smooths the transitions between OFDM symbols.
For Windowing = N samples, the cyclic prefix added to the nominal OFDM symbol extends by N additional samples. This extended waveform is windowed by pointwise multiplication in the time domain with a raised cosine window, which applies a taper to the first N and last N samples, with all other values being 1. The windowed OFDM symbols are then overlapped by commencing transmission of each windowed OFDM symbol N samples before the end of the previous OFDM symbol. This overlapping ensures that the time between OFDM symbols is maintained as required by the standard. The taper at the start of the first OFDM symbol for transmission is removed and is overlapped with the taper at the end of the last OFDM symbol.
Filter
Filter settings allow to filtering the waveform in order to achieve a finite bandwidth and improve the spectral efficiency.
Before introducing the Filtering, we will start with the two other setting:
Rolloff factor : defines the filter rolloff. 0<rolloff factor<1.
Filter span : defines the number of symbols truncated. 0<filter span.
Filtering : Three filtering options are available in the Waveform Ganerator :
Resource Mapping
Resource Mapping section allows to define the sub-carriers index, symbol index and resource modulation type (Arbitrary binary sequence, QPSK, 8PSK 16/32/64/128/256/512/1024/2048/4096 QAM) of each preamble, pilot, and data added.
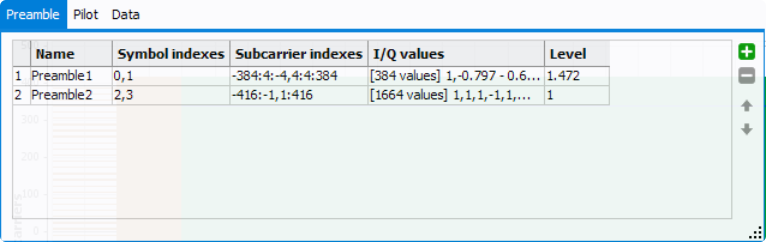
- Preamble
Use
 to add new preamble and
to add new preamble and  to delete one. Use
to delete one. Use  and
and  to moves the selected resource
configuration up and down one position in the resource list.
to moves the selected resource
configuration up and down one position in the resource list.
1) Name: Specify the name of the selected Preamble resource block.
2) Symbol Indexes: Set the symbol index for the selected Preamble resource block. There are three ways to configure symbols:
-
To configure by individual symbol, use a comma (,) as the delimiter. For example, 0,1,2,3.
-
To configure by a range of symbols, use a colon (:) to indicate the start symbol index and the end symbol index. For example, 3:10 means symbols 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
-
To configure by a certain step, use two colons (:) to indicate the start symbol index, the step, and the end symbol index. For example, 0:5:20 means symbols 0,5,10,15,20.Note: Combination of tree can be used. Example: -21:7:-1,1:7:21 gives -21,-14,-7,-1,1,7,14,21
-
To configure by individual symbol, use a comma (,) as the delimiter. For example, 0,1,2,3.
-
To configure by a range of symbols, use a colon (:) to indicate the start symbol index and the end symbol index. For example, 3:10 means symbols 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
-
To configure by a certain step, use two colons (:) to indicate the start symbol index, the step, and the end symbol index. For example, 0:5:20 means symbols 0,5,10,15,20.Note: Combination of tree can be used. Example: -21:7:-1,1:7:21 gives -21,-14,-7,-1,1,7,14,21
-
- 4) Select the data mode for pilot. Pilot pattern can be defined in two
ways:
- User can input pilot IQ values, enabling I/Q
column.
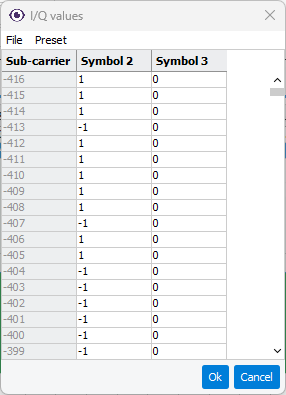
Opens an editor (
 ) to configure IQ values transmitted
in Pilot resource block type.
) to configure IQ values transmitted
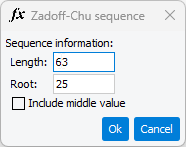
in Pilot resource block type.Clicking the Preset drop-down menu allows you to select Zadoff-Chu, which opens an editor for configuring a Zadoff-Chu sequence onto the sub-carriers.
Zadoff-Chu root sequence is generated with:
- Sequence Length (L): Number of values in the sequence.
- Root Index (q): The root index of the sequence.
- Include Middle Value: When checked, the value with the middle index (L/2) will be included in the sequence.
- Specify the payload bits with a modulation scheme, disabling
I/Q column.
Select the modulation scheme used for the resource block using Constellation column. The drop-down list contains all the constellations (QPSK, 8PSK 16/32/64/128/256/512/1024/2048/4096 QAM).
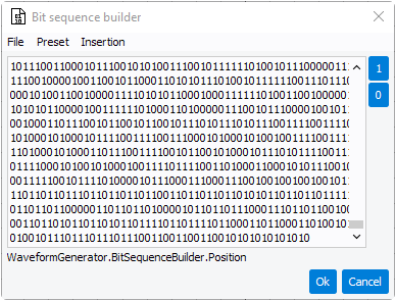
In Bit sources columns select payload bits to be modulated in Pilot or Data resource block type (PN9, PN15, PN21, Random). You can also create custom play load or load, save, and create custom bit patterns, selecting "Custom" and press on
 icon.
icon.
- User can input pilot IQ values, enabling I/Q
column.
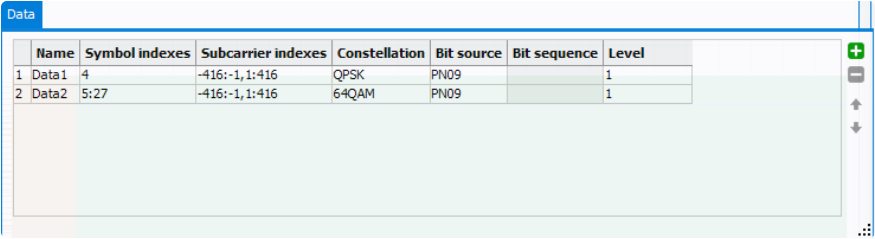
- Data
Use
 to add new data and
to add new data and  to delete one. Use
to delete one. Use  and
and  to moves the selected resource
configuration up and down one position in the resource list.1) Name: Specify the name of the selected Data resource block.
to moves the selected resource
configuration up and down one position in the resource list.1) Name: Specify the name of the selected Data resource block.
2) Symbol Indexes: Set the symbol index for the selected Data resource block. There are three ways to configure symbols:
-
To configure by individual symbol, use a comma (,) as the delimiter. For example, 0,1,2,3.
-
To configure by a range of symbols, use a colon (:) to indicate the start symbol index and the end symbol index. For example, 3:10 means symbols 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
-
To configure by a certain step, use two colons (:) to indicate the start symbol index, the step, and the end symbol index. For example, 0:5:20 means symbols 0,5,10,15,20.Note: Combination of tree can be used. Example: -21:7:-1,1:7:21 gives -21,-14,-7,-1,1,7,14,21
-
To configure by individual symbol, use a comma (,) as the delimiter. For example, 0,1,2,3.
-
To configure by a range of symbols, use a colon (:) to indicate the start symbol index and the end symbol index. For example, 3:10 means symbols 3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10.
-
To configure by a certain step, use two colons (:) to indicate the start symbol index, the step, and the end symbol index. For example, 0:5:20 means symbols 0,5,10,15,20.Note: Combination of tree can be used. Example: -21:7:-1,1:7:21 gives -21,-14,-7,-1,1,7,14,21
4) Constellation: Select the modulation scheme used for the resource block using Constellation column. The drop-down list contains all the constellations (QPSK, 8PSK 16/32/64/128/256/512/1024/2048/4096 QAM).
In Bit sources columns select payload bits to be modulated in Pilot or Data resource block type (PN9, PN15, PN21, Random). You can also create custom play load or load, save, and create custom bit patterns, selecting "Custom" and press on
 icon.5) Level : Set the amplitude boost level for the modulated symbols in the resource block, in linear value. e.g. original symbol 1+i with boost level 2.5 will be 2.5+2.5i.
icon.5) Level : Set the amplitude boost level for the modulated symbols in the resource block, in linear value. e.g. original symbol 1+i with boost level 2.5 will be 2.5+2.5i.
-