Wafer
Overview
The (
Click on the (
How it works
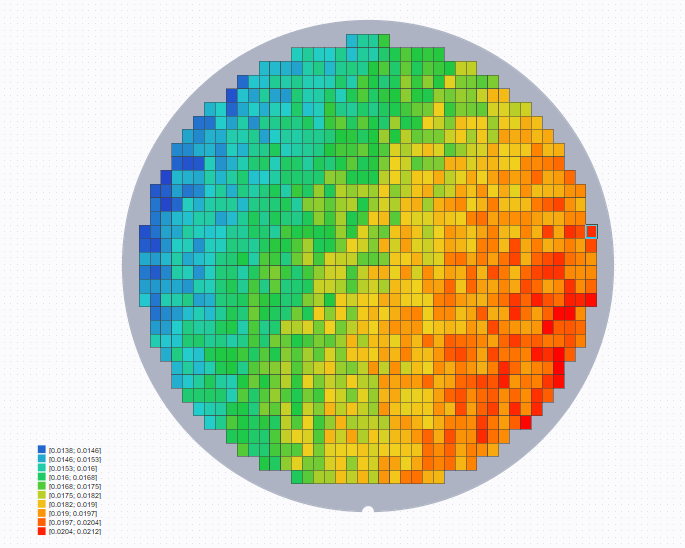
On 'Wafer' control, there are three possibilities of die display:
Empty: no measurement has been performed for this position
Colored: only one measurement has been performed for this position
Cross: more than one measurement for this position. Filter can be used to display results on each die.
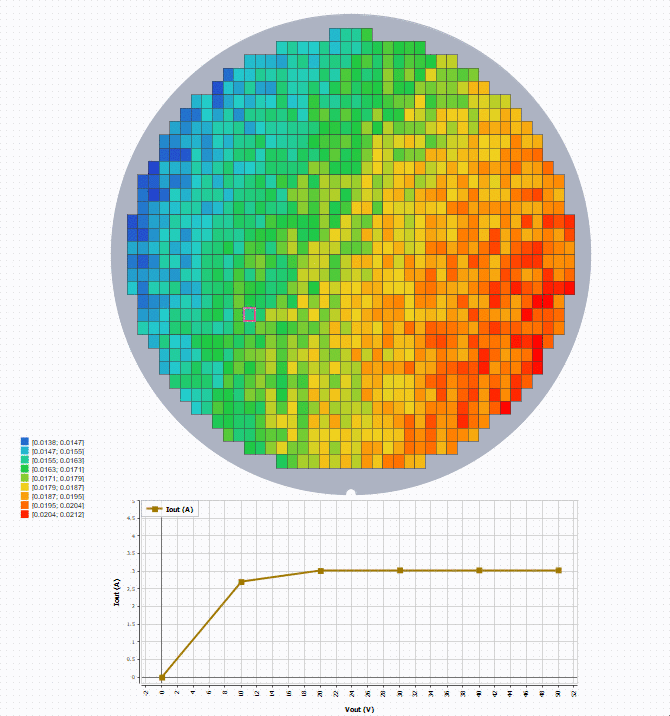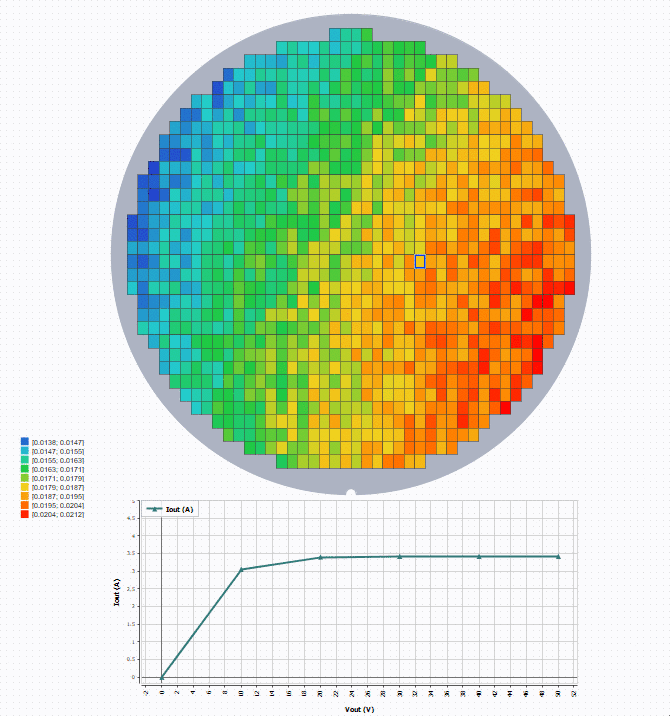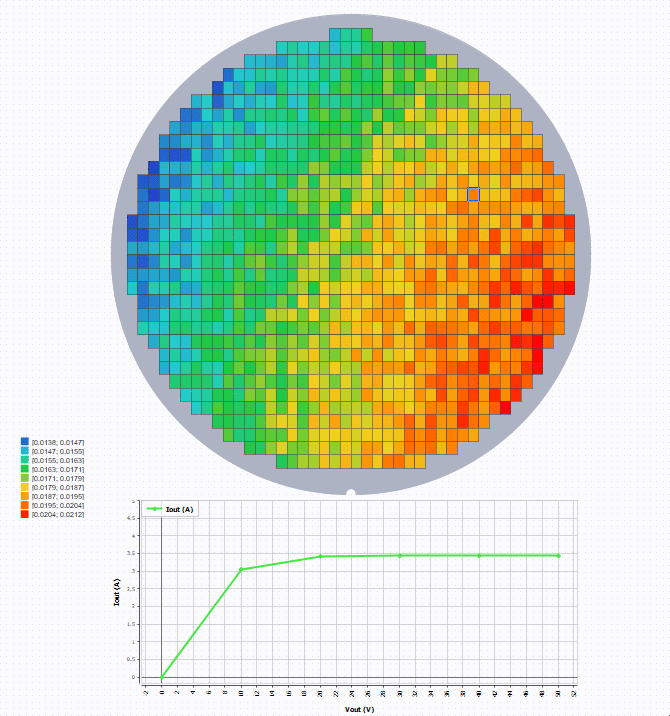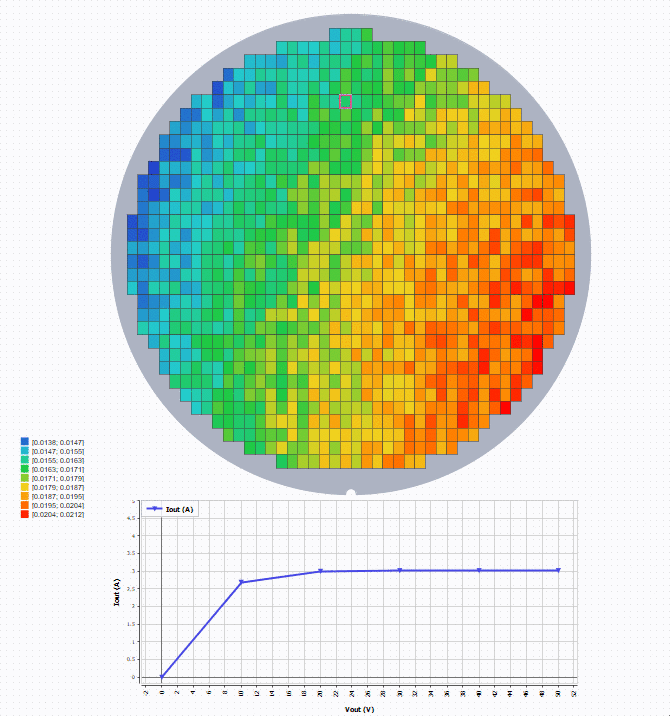
To see the curve at a specific die position, create and configure a Graph with wafer as the source. Then select a position to show
the curve.

Display
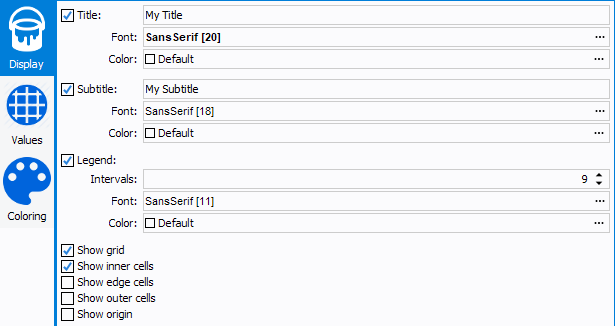
- Title: title of the wafer, will be displayed on top of the control
- Title Font
- Title Color
- Subtitle: subtitle of the wafer, will be displayed on top of the
control, under the title
- Subtitle Font
- Subtitle Color
- Legend: legend of the wafer, will be displayed in the bottom left
corner
- Intervals: Number of ranges to display (min 0, max 20), the higher the number is, the higher the precision will be.
- Legend Font
- Legend Color
- Show grid: display the grid (useful for delimiting dies)
- Show inner cells: show dies inside the wafer (required to display values)
- Show edge cells: show wafer outline dies (not measured)
- Show outer cells: show dies outside the wafer (not measured)
- Show origin: show the die at the position 0;0
Values
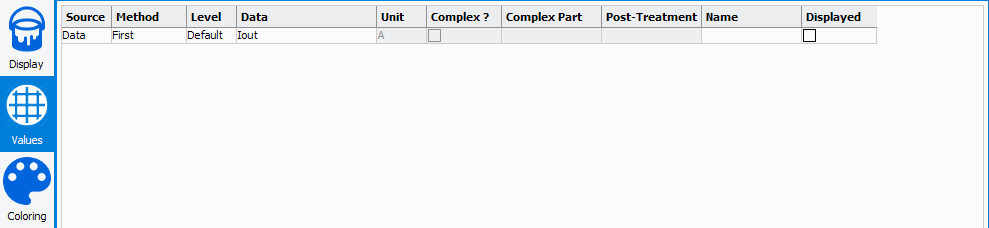
Here can be defined the values to display on each die. The main board can be parametrized as follows:
- Source: select whether the parameter is a variable or data
- Method: select the method of extraction ('Interpolation', 'Minimum', 'Maximum', 'First', 'Last', 'Average', 'Sum')
- Level: select the frequency level corresponding to the data to
displayNote: The level setting is done to sort the data when harmonics (Level : f0, 2.f0, 3.f0 ...) or 2-tones (Level : 2.f2-f1, f1, f2, 2.f1-f2 ...) measurements analysis are required.
- Data: select the parameter to displayNote: The data list depends on the *.imx file loaded in the 'Datasource, on the 'Allowed curves' defined and on the 'Level' selected. The data list is sorted by alphabetical order.
- Unit: select the unit of the parameter to displayNote: The unit list depends on the data selected.
- Complex: check if the value is a complex and unlocks the following parameter.
- Complex Part: select the complex part corresponding to the parameter to display when this one is a complex number (A1,B1,A2,B2, Zin, Zload, ...).
- Post-treatment: allows to invert the sign
- Custom name: choose a custom name
Then, under the board, the following settings are defined:
- Show values: show the value on the die
- Values notation: how will values be displayed
- Values precision: number of digits
- Adaptive precision: when checked, the number of digit in the floating part depends of the value of the integer part; the precision is reduced when the integer part grows up
- Force sign: force the display of the value sign
- Opposite color for the values text: adjusts font color to background color (e.g. write text in white if the background color is black)
Coloring
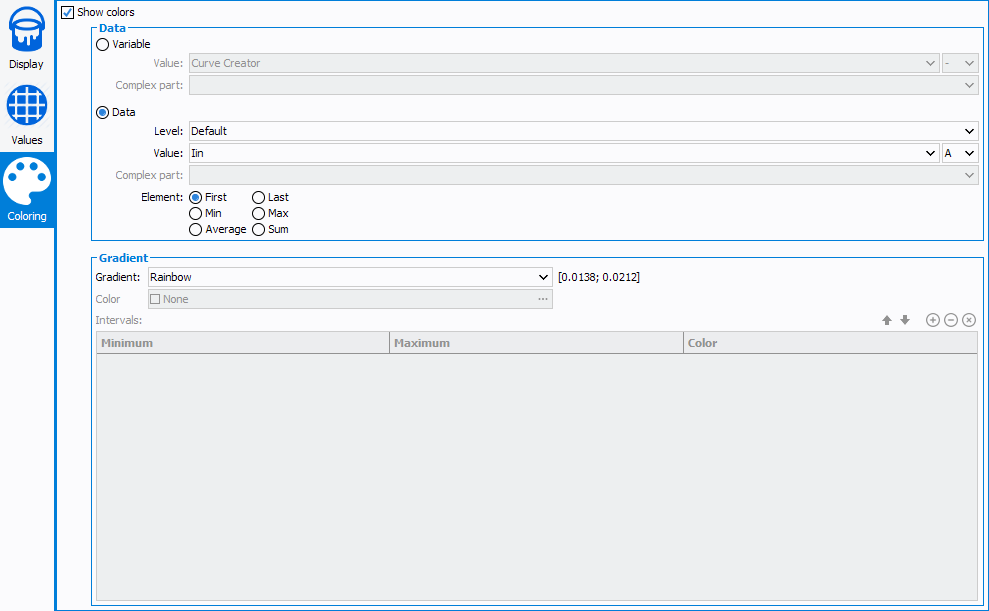
- Show color: enables the configuration of the wafer coloration
- Data editor: define the data to display, can be either Variable or Data
- Gradient editor: define behavior of colors
- Gradient: types of gradient will be used
- Rainbow: blue to red colors (minimum to maximum)
- Gray-scale: black and white rainbow, white to black (minimum to maximum)
- One color: use only one color (defined thereafter), not compliant with 'interval count' option
- Intervals: defines custom intervals (defined thereafter), not compliant with 'interval count' option
- Color: used by One color gradient to define the color to display
- Intervals: used by Intervals gradient to
define the intervals to display
: add a new interval
: remove selected intervals
: clear all intervals
: move interval above
: move interval below
Note: Empty minimum or maximum cell will use infinite value
- Gradient: types of gradient will be used
Example
Here is an example of a wafer being a source of a Graph, that allows (with a selection of a die) to
display on a graph some curves.